Migration From On-Premises to Cloud: Best Practices Guide




Migrating IT infrastructures to the cloud can be intricate and may slow down a company’s growth. Let’s consider the main aspects of moving the IT infrastructure and the benefits for the company.
Before diving into the migration process, it’s crucial to understand the various strategies available and their implications for your business.
Cloud migration strategies are often categorized into six main approaches, known as the “6 Rs”:
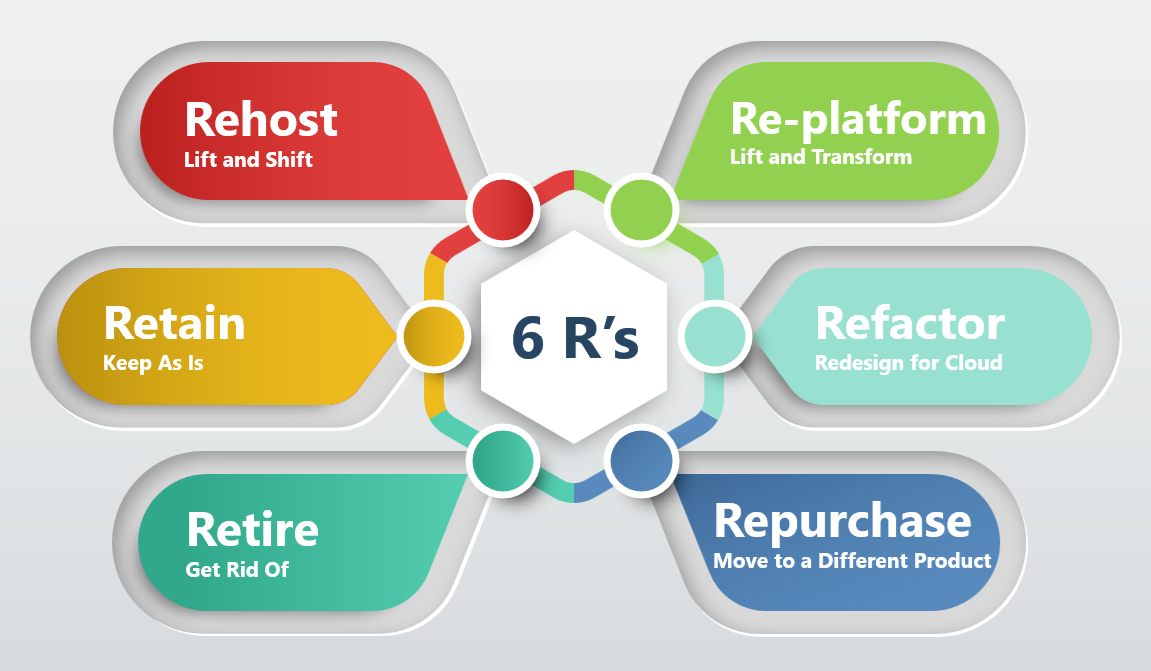
Rehost (Lift and Shift): This approach involves moving applications to the cloud without making significant changes. It’s the fastest and most cost-effective option for applications that work well on-premises and don’t require major modifications.
Replatform (Lift and Transform): This strategy involves making some optimizations to take advantage of cloud-native features without completely overhauling the application architecture.
Refactor (Redesign for Cloud): This approach involves re-architecting applications to fully leverage cloud-native features and services.
Repurchase (Move to a Different Product): The repurchase strategy, sometimes referred to as “drop and shop,” involves moving to a different product, typically by switching to a cloud-native solution or a Software as a Service (SaaS) application.
Retire (Get Rid Of): This involves identifying and decommissioning applications that are no longer needed.
Retain (Keep As Is): Some applications may need to remain on-premises due to compliance, technical, or business reasons.
For businesses seeking flexibility and resilience, hybrid and multi-cloud strategies offer compelling options:
To choose and plan your “move” to the cloud effectively, you should first consider:
Based on these factors, you can select the most appropriate tool. Here are the main types of cloud data migration:
P2V (Physical to Virtual)
This involves converting a physical server into a virtual one, commonly needed in enterprises transitioning from standalone servers to virtualization systems.
P2C (Physical to Cloud)
This migration transforms a physical server into a cloud-based one, directly moving data to cloud IaaS resources. It’s relevant for companies deciding between purchasing servers or opting for cloud services to avoid capital expenditure.
V2V (Virtual to Virtual)
Required when switching between different virtualization platforms due to changes in corporate standards or when consolidating various virtualization infrastructures. It’s also relevant when moving to the cloud if the cloud’s virtualization system differs from the existing one.
V2C (Virtual to Cloud)
This migration shifts virtual machines to the cloud. The size of the VM is crucial, as is the data transfer method. Before initiating such migrations, analyze your software for built-in data transfer capabilities to possibly simplify the process.
Optimized Resource Allocation: Cloud services deliver resources precisely when and where they’re needed, eliminating waste and ensuring efficiency at every step.
Predictable, Transparent Costs: You only pay for the resources you actually consume (computing power, network bandwidth, storage), making budgeting and scaling costs predictable as your business grows.
Simplified IT Management: Reduce your IT burden. Cloud services streamline management, often requiring only a small team (or even a single person) to handle tasks that previously demanded a large IT department.
Round-the-Clock Expert Support: Access immediate, expert technical assistance anytime with cloud providers’ 24/7 support and specialized engineering teams.
Simple Migration Between Providers: Easily switch cloud providers if a better offer comes along. Migrating your data and applications is straightforward, giving you control and preventing vendor lock-in.
Mobility: Access your data and applications from anywhere in the world. Cloud services eliminate geographical constraints, simplifying operations when you expand or relocate.
Uninterrupted Service: Benefit from robust cloud infrastructure, expert management, comprehensive backups, and emergency power systems that minimize downtime and ensure continuous availability.
Disaster Recovery: Cloud solutions often include robust disaster recovery options, ensuring business continuity during outages or data loss.
A successful cloud migration begins with thorough planning and preparation.
Assess and Prioritize
Start by evaluating your existing IT infrastructure, applications, and workloads. This assessment helps identify critical workloads, dependencies, and potential migration challenges. Prioritize applications based on their complexity, business value, and suitability for cloud migration.
Define Clear Goals and Objectives
Establish measurable objectives for your migration, including performance targets, cost savings, and timeline expectations. Align these goals with your broader business strategy and get buy-in from both technical and business leaders.
Choose the Right Cloud Provider
Carefully evaluate cloud providers based on your specific needs, considering factors such as pricing models, available services, compliance capabilities, and future roadmaps. Don’t just focus on list prices – consider reserved instances, commit discounts, and migration incentives offered by providers. Consider cloud features:
Develop a Comprehensive Migration Plan
Create a detailed plan that outlines the resources, timelines, and responsibilities for each phase of the migration process. Include risk mitigation measures and contingency plans to address potential challenges. Don’t forget to establish rollback thresholds and plans in case of unforeseen issues.
With a solid plan in place, it’s time to execute your cloud migration strategy.
Start with a Pilot Project
Begin with a small-scale pilot migration to test your approach and identify any potential issues. This allows you to refine your strategy before tackling more complex or critical workloads.
Implement Strong Security Measures
Security is paramount during and after migration. Implement robust encryption, access controls, and compliance measures to protect your data throughout the process. Pay special attention to industry-specific regulations and privacy laws that may impact your migration strategy.
Address Skill Gaps and Training
Cloud migration requires specialized skills and expertise. Invest in training for your team and consider partnering with experienced cloud consultants to fill any knowledge gaps. Effective change management and pre-migration training are crucial for ensuring a smooth transition.
Optimize Resource Management and Scalability
Configure your cloud environment to meet both immediate demands and future scalability needs. Properly set up auto-scaling features to handle unexpected traffic surges and maintain optimal performance.
Continuously Monitor and Optimize
After migration, implement robust monitoring tools to track performance, costs, and security in your new cloud environment. Continuously optimize your cloud infrastructure to maximize efficiency and adapt to evolving business needs.
While cloud migration offers numerous benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential challenges:
Migrating from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud is a transformative journey that can drive significant benefits for your business. By carefully planning your migration strategy, addressing potential challenges, and following best practices, you can ensure a smooth transition that sets your organization up for long-term success in the cloud.
Remember, cloud migration is not a one-time event but an ongoing process of optimization and innovation. Stay agile, continuously monitor your cloud environment, and be prepared to adapt your strategy as your business needs evolve.
We specialize in DevOps as a Service, combining industry-leading best practices with tailored solutions to optimize workflows, enhance scalability, and ensure seamless infrastructure performance. We are here to transform your DevOps processes into a strategic advantage. Whether you’re scaling operations or refining deployment pipelines, our team will deliver the technical expertise and proactive support you need.

Learn how our experts can accelerate your business growth with DevOps as a Service offering